このガイドでは、次のことを行います:
- ベクトル検索の概要を簡単に押さえる
- 近似最近傍探索 (Approximate Nearest Neighbours; ANN) と Hierarchical Navigable Small World (HNSW) について学ぶ
- Quantised Bit (QBit) について学ぶ
- QBit を使用して、DBPedia データセットに対してベクトル検索を実行する
ベクトル検索入門
数学や物理学において、ベクトルは大きさと向きをあわせ持つ対象として形式的に定義されます。
これはしばしば線分や空間中の矢印として表現され、速度・力・加速度などの量を表すために使われます。
計算機科学において、ベクトルは有限個の数値の並びです。
言い換えると、数値を格納するために用いられるデータ構造です。
機械学習においても、ベクトルは計算機科学で扱うものと同じデータ構造ですが、その中に格納される数値には特別な意味があります。
テキストの塊や画像を取り、そこに含まれる主要な概念を抽出して数値として表現する処理は、エンコード (encoding) と呼ばれます。
その結果として得られる出力は、主要な概念を機械が数値として表現したものです。
これが「埋め込み (embedding)」であり、ベクトルとして保存されます。
別の言い方をすると、この文脈上の意味がベクトルに埋め込まれているとき、それを埋め込み (embedding) と呼ぶことができます。
ベクトル検索は今やあらゆるところで利用されています。
音楽のレコメンデーション、大規模言語モデルが外部知識を取り込んで回答を改善する retrieval-augmented generation (RAG)、さらには Google 検索も一部は、ベクトル検索によって支えられています。
専用のベクトルデータベースには利点があるにもかかわらず、多くのユーザーは完全に特化したベクトルストアよりも、アドホックにベクトル機能を備えた一般的なデータベースを好みます。
ClickHouse は、総当たりによるベクトル検索に加えて、HNSW を含む近似最近傍 (ANN: Approximate Nearest Neighbour) 検索のための手法もサポートしており、これは高速なベクトル検索の現在の標準的な方式となっています。
埋め込みを理解する
ベクトル検索がどのように動作するのかを理解するために、簡単な例を見てみましょう。
単語の埋め込み(ベクトル表現)について考えてみます:
以下のテーブルを作成し、いくつかのサンプル埋め込みを用意します:
CREATE TABLE fruit_animal
ENGINE = MergeTree
ORDER BY word
AS SELECT *
FROM VALUES(
'word String, vec Array(Float64)',
('apple', [-0.99105519, 1.28887844, -0.43526649, -0.98520696, 0.66154391]),
('banana', [-0.69372815, 0.25587061, -0.88226235, -2.54593015, 0.05300475]),
('orange', [0.93338752, 2.06571317, -0.54612565, -1.51625717, 0.69775337]),
('dog', [0.72138876, 1.55757105, 2.10953259, -0.33961248, -0.62217325]),
('horse', [-0.61435682, 0.48542571, 1.21091247, -0.62530446, -1.33082533])
);
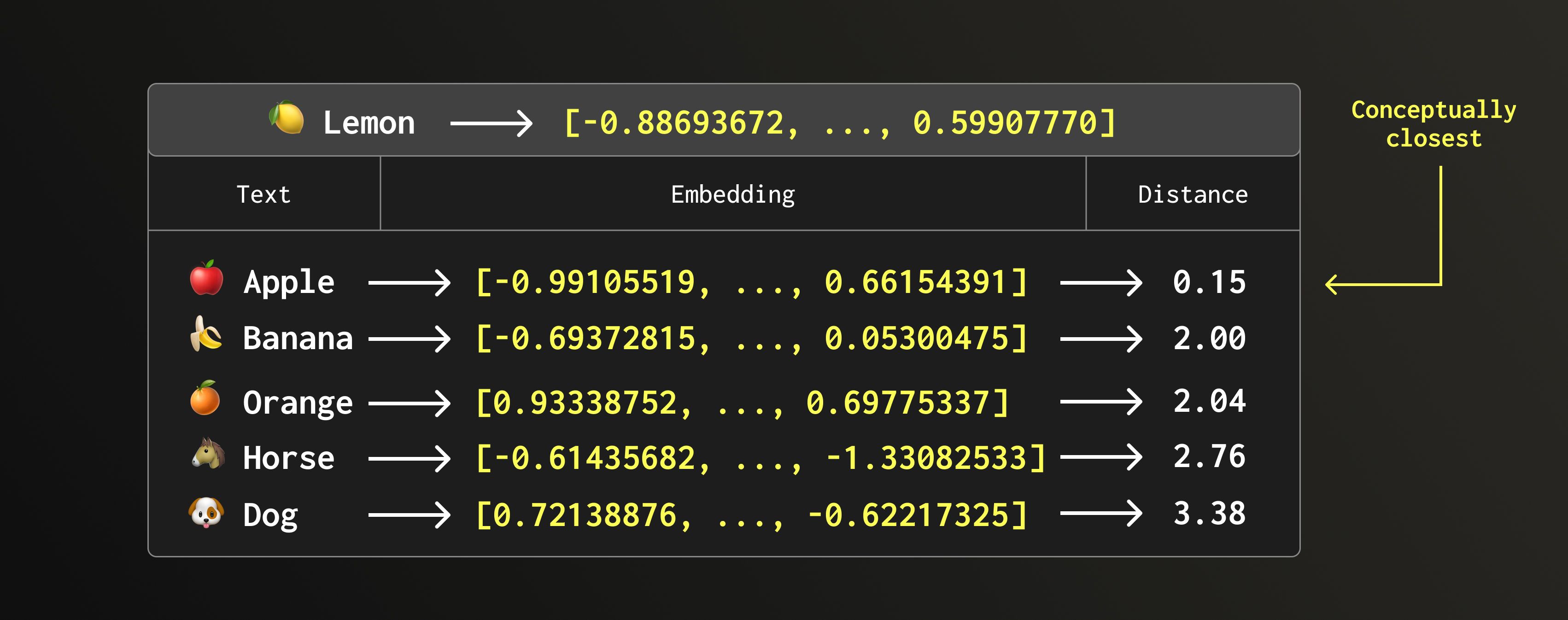
与えられた埋め込みベクトルに最も近い単語を検索できます。
SELECT word, L2Distance(
vec, [-0.88693672, 1.31532824, -0.51182908, -0.99652702, 0.59907770]
) AS distance
FROM fruit_animal
ORDER BY distance
LIMIT 5;
┌─word───┬────────────distance─┐
│ apple │ 0.14639757188169716 │
│ banana │ 1.9989613690076786 │
│ orange │ 2.039041552613732 │
│ horse │ 2.7555776805484813 │
│ dog │ 3.382295083120104 │
└────────┴─────────────────────┘
クエリの埋め込みは「apple」の埋め込みに最も近く(距離が最小)、2つの埋め込みを並べて見ると、それも納得できるはずです。
apple: [-0.99105519,1.28887844,-0.43526649,-0.98520696,0.66154391]
query embedding: [-0.88693672,1.31532824,-0.51182908,-0.99652702,0.5990777]
近似最近傍探索 (ANN)
巨大なデータセットに対しては、総当たり検索は処理が遅くなりすぎます。
ここで役立つのが、Approximate Nearest Neighbours(ANN)手法です。
Quantisation
Quantisation では、数値型をより小さい型へダウンキャストします。
より小さい数値型を使うとデータ量が小さくなり、データ量が小さくなると距離計算が高速になります。
ClickHouse のベクトル化クエリ実行エンジンは、1 回の処理でより多くの値をプロセッサのレジスタに収められるため、スループットがそのまま向上します。
選択肢は 2 つあります:
- 元のカラムと並行して量子化したコピーを保持する - ストレージ使用量は 2 倍になりますが、常にフル精度のデータにフォールバックできるため安全です
- 元の値を完全に置き換える(挿入時にダウンキャストする) - 容量と I/O を節約できますが、後戻りはできません
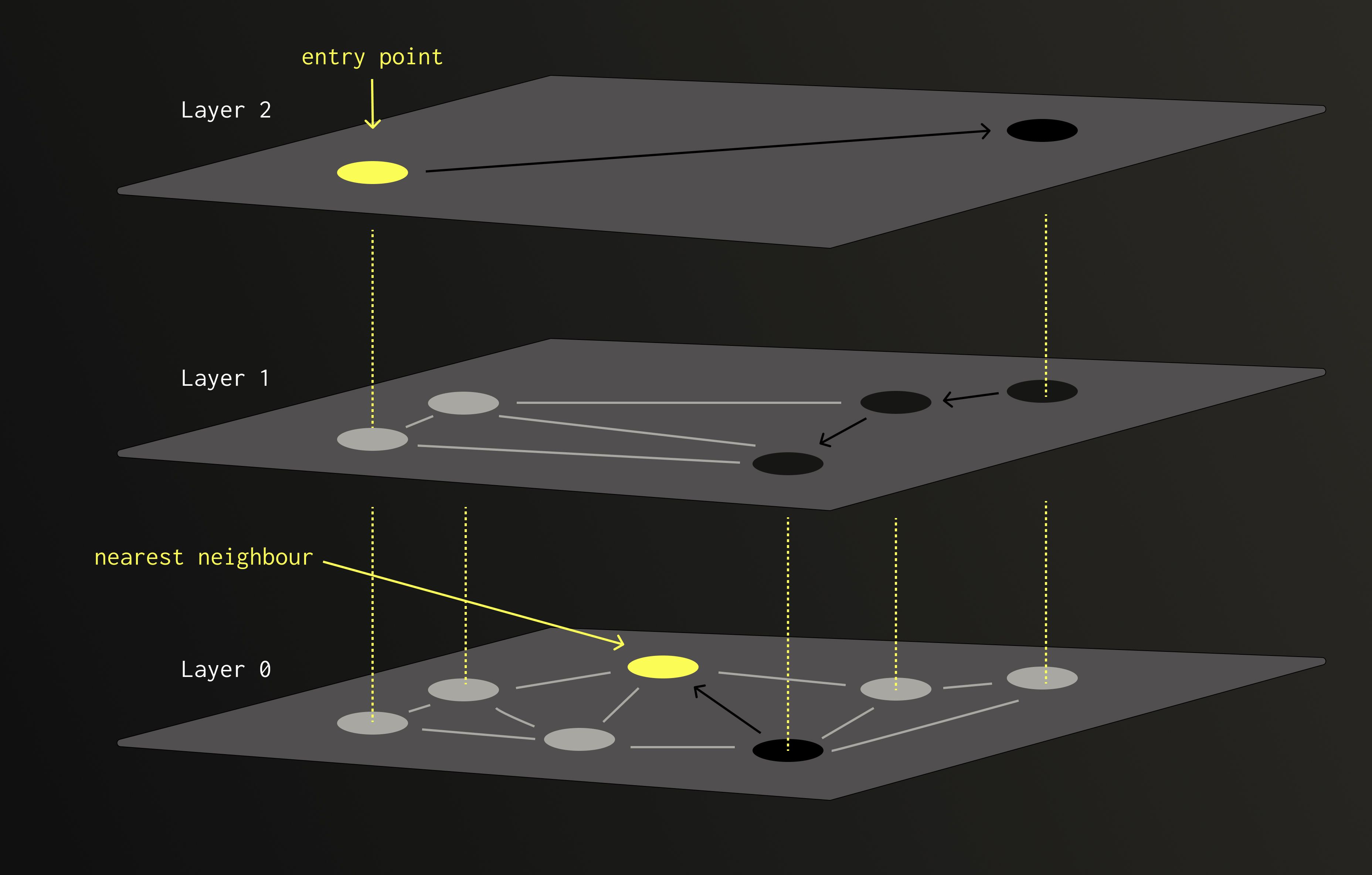
Hierarchical Navigable Small World (HNSW)
HNSW は複数のレイヤーから成るノード(ベクトル)の階層構造として構築されます。各ノードは 1 つ以上のレイヤーにランダムに割り当てられ、高いレイヤーに出現する確率は指数関数的に減少します。
検索を行う際は、最上位レイヤーのノードから開始し、最も近い近傍に向かって貪欲に移動します。これ以上近いノードが見つからなくなったら、次のより高密度なレイヤーに降りていきます。
このようなレイヤー構造の設計により、HNSW はノード数に対して対数オーダーの検索計算量を実現します。
HNSW の制約
主なボトルネックはメモリです。ClickHouse は HNSW の実装として usearch を使用しており、これは分割をサポートしないインメモリのデータ構造です。
その結果、大規模なデータセットではそれに応じて多くの RAM が必要になります。
手法の比較
| カテゴリ | Brute-force | HNSW | QBit |
|---|
| 精度 | 完全 | 高い | 柔軟 |
| 速度 | 低速 | 高速 | 柔軟 |
| その他 | 量子化:より多くの容量を消費、もしくは不可逆な精度低下 | 索引をメモリに載せる必要があり、構築も必要 | 依然として O(レコード数) |
QBit の詳細
Quantised Bit (QBit)
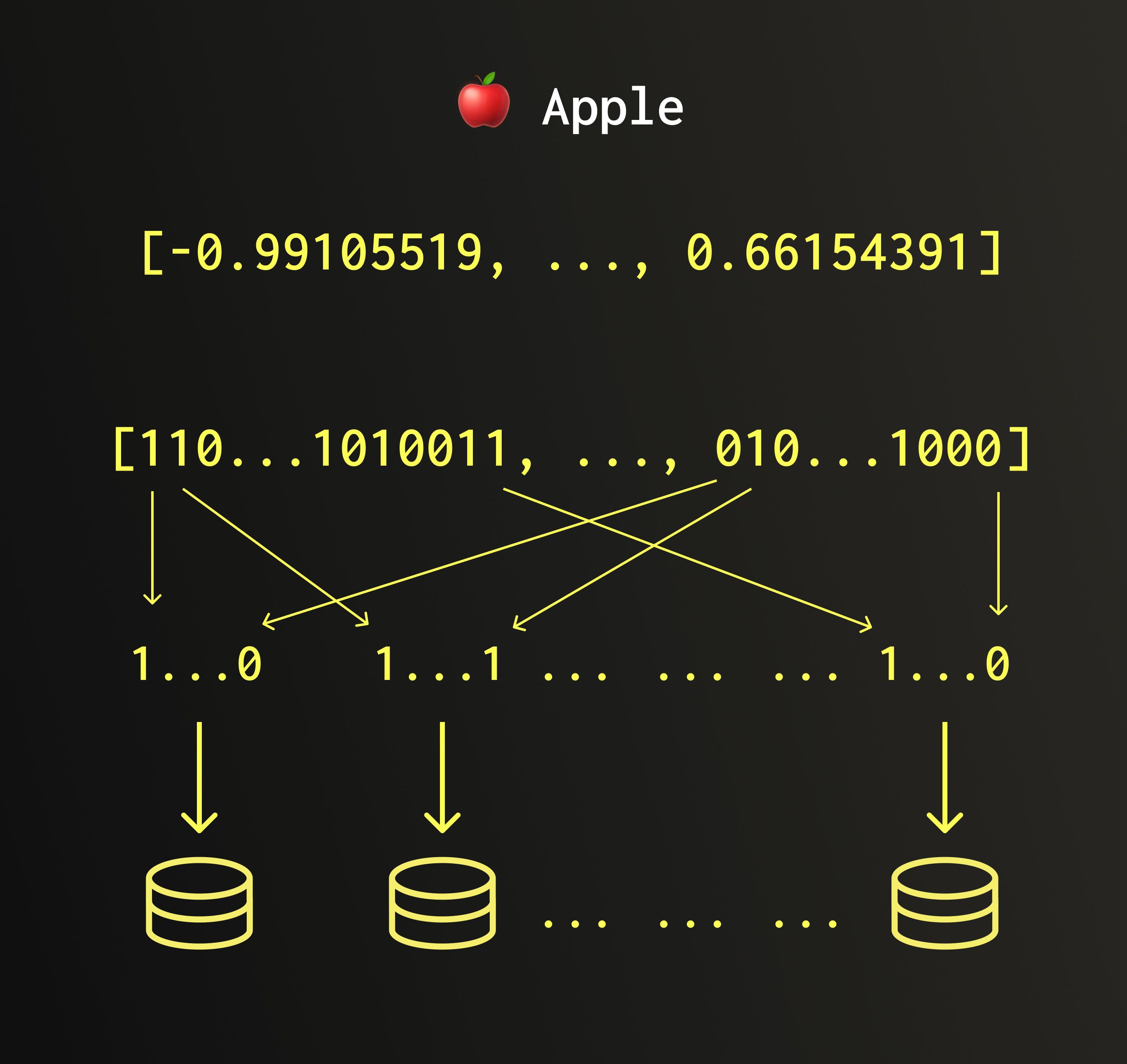
QBit は、新しいデータ構造であり、浮動小数点数がビット列として表現される仕組みを活用して BFloat16、Float32、Float64 の値を格納できます。
各数値をそのまま格納するのではなく、QBit は値をビットプレーンに分割します。各値の第 1 ビット、各値の第 2 ビット、各値の第 3 ビット、というようにです。
このアプローチにより、従来の量子化の主な制約が解消されます。重複したデータを保存する必要もなく、値が意味を失うリスクもありません。また、QBit はインメモリのインデックスを維持するのではなく、保存されているデータを直接操作するため、HNSW の RAM ボトルネックも回避できます。
利点
何よりも重要なのは、事前の設計上の決定が不要であることです。
精度とパフォーマンスはクエリ実行時に動的に調整でき、ユーザーは精度と速度のバランスを、ほとんど負担なく試行・探索できます。
制約
QBit はベクトル検索を高速化しますが、その計算量は依然として O(n) のままです。言い換えると、データセットが十分小さく、HNSW のインデックスを RAM に余裕を持って収められる場合は、依然としてそれが最速の選択肢です。
データ型
QBit カラムを作成するには、次のようにします。
SET allow_experimental_qbit_type = 1;
CREATE TABLE fruit_animal
(
word String,
vec QBit(Float64, 5)
)
ENGINE = MergeTree
ORDER BY word;
INSERT INTO fruit_animal VALUES
('apple', [-0.99105519, 1.28887844, -0.43526649, -0.98520696, 0.66154391]),
('banana', [-0.69372815, 0.25587061, -0.88226235, -2.54593015, 0.05300475]),
('orange', [0.93338752, 2.06571317, -0.54612565, -1.51625717, 0.69775337]),
('dog', [0.72138876, 1.55757105, 2.10953259, -0.33961248, -0.62217325]),
('horse', [-0.61435682, 0.48542571, 1.21091247, -0.62530446, -1.33082533]);
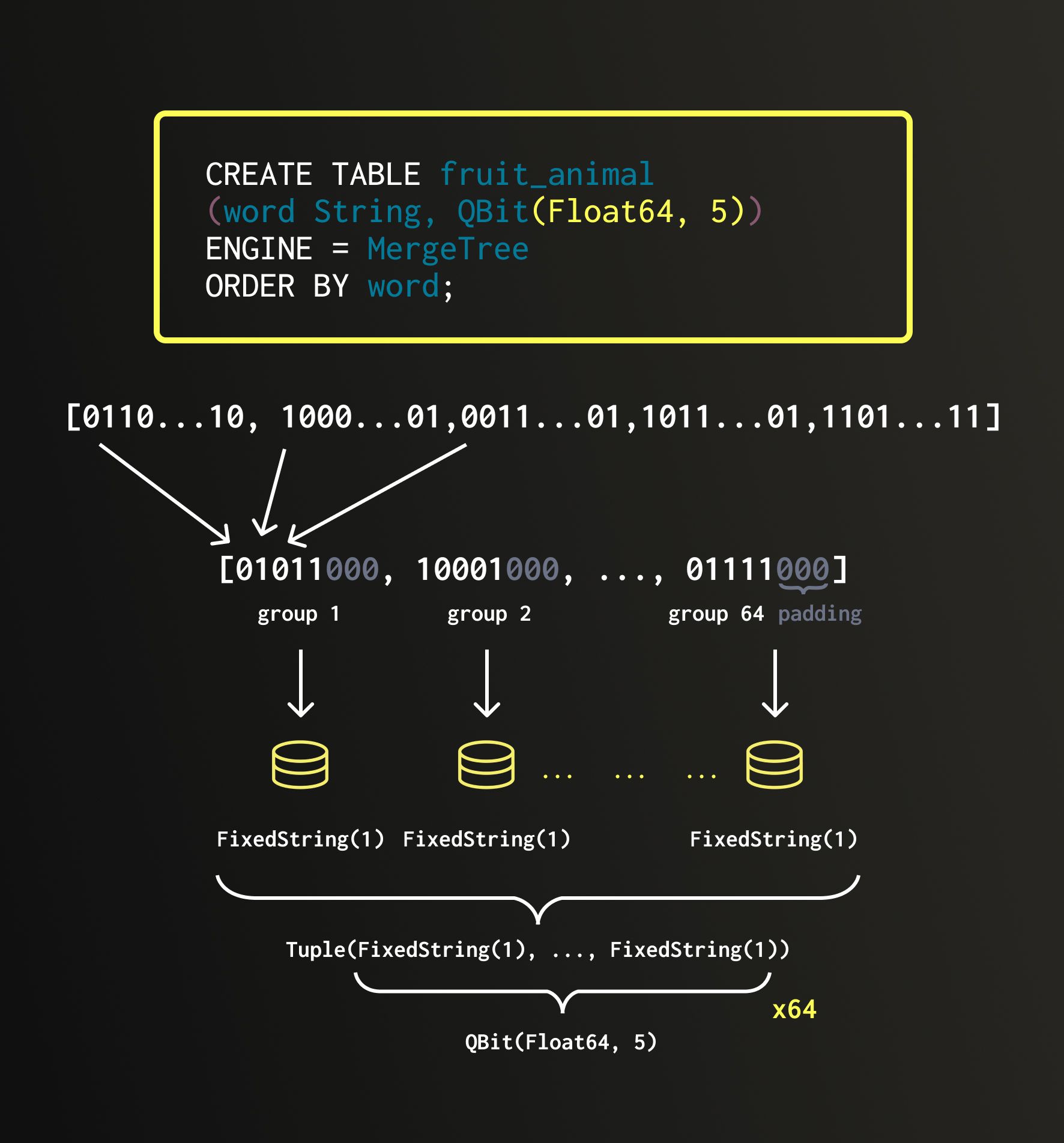
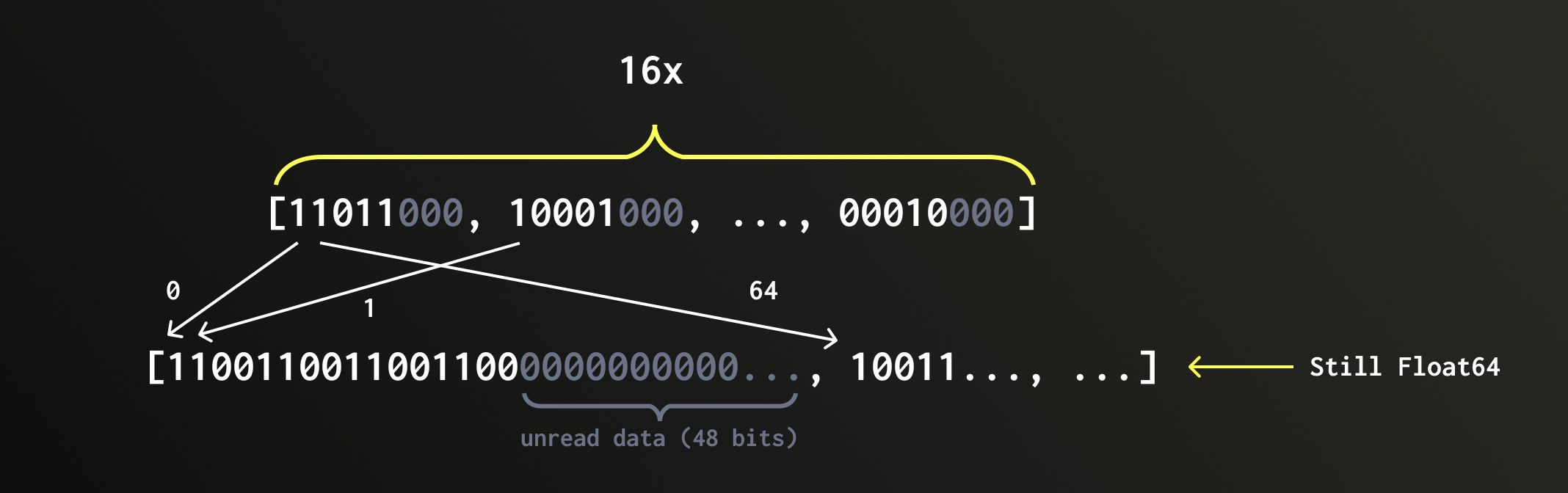
データが QBit カラムに挿入されると、すべての1ビット目がそろい、すべての2ビット目がそろい、というように転置されます。これらを グループ と呼びます。
各グループは個別の FixedString(N) カラムに保存されます。これは、区切り文字なしでメモリ上に連続して格納される、長さ N バイトの固定長文字列です。これらすべてのグループは 1 つの Tuple にまとめられ、これが QBit の基盤となるデータ構造を形成します。
例: 8×Float64 要素からなるベクトルを入力とすると、各グループは 8 ビットを含みます。Float64 は 64 ビットあるため、最終的には 64 個のグループ(各ビットにつき 1 グループ)になります。したがって、QBit(Float64, 8) の内部レイアウトは、64×FixedString(1) カラムからなる Tuple になります。
ヒント
元のベクトル長が 8 で割り切れない場合、構造は 8 に揃うように見えない要素でパディングされます。これは、FixedString が完全なバイト単位でのみ動作するという制約に合わせるためです。
距離計算
QBit でクエリするには、精度パラメータを指定して L2DistanceTransposed 関数を使用します。
SELECT
word,
L2DistanceTransposed(vec, [-0.88693672, 1.31532824, -0.51182908, -0.99652702, 0.59907770], 16) AS distance
FROM fruit_animal
ORDER BY distance;
┌─word───┬────────────distance─┐
│ apple │ 0.15196434766705247 │
│ banana │ 1.966091150410285 │
│ orange │ 1.9864477714218596 │
│ horse │ 2.7306267946594005 │
│ dog │ 3.2849989362383165 │
└────────┴─────────────────────┘
3 つ目のパラメータ (16) は、ビットでの精度レベルを指定します。
I/O 最適化
距離を計算する前に、必要なデータをディスクから読み出し、その後転置を解除(ビットをグループ化した表現から元のベクトル表現に戻す)する必要があります。QBit は値を精度レベルごとにビット転置して保存しているため、ClickHouse は目的の精度までの数値を再構築するのに必要な上位ビットプレーンだけを読み取ることができます。
上記のクエリでは、精度レベル 16 を使用しています。Float64 は 64 ビットなので、最初の 16 ビットプレーンだけを読み込み、データの 75% をスキップします。
読み込み後、ロードされたビットプレーンから各数値の上位部分だけを再構築し、未読み込みのビットは 0 のまま残します。
計算の最適化
Float32 や BFloat16 のような、より小さい型にキャストすることで、この未使用部分を取り除けないかと考えるかもしれません。これは有効ですが、すべての行に対して明示的なキャストを行うと高コストになります。
代わりに、参照ベクターだけをダウンキャストし、QBit データはより狭い値を含んでいるかのように扱います(いくつかのカラムが存在しないものとして扱うイメージです)。これは、そのレイアウトがしばしばそれらの型を切り詰めたものに対応しているためです。
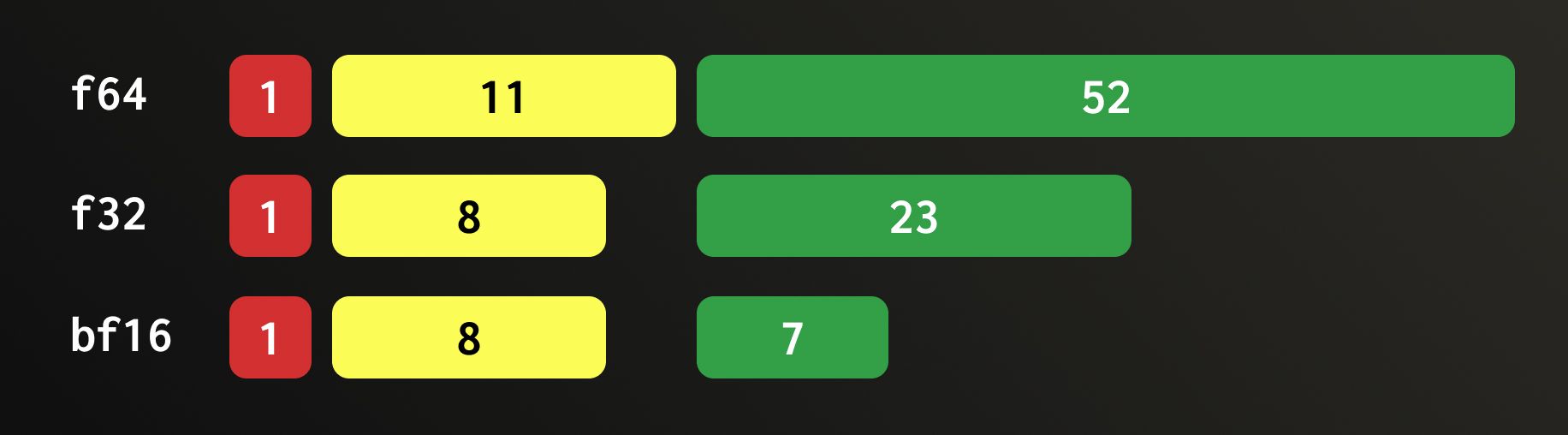
BFloat16 の最適化
BFloat16 は、Float32 の下位ビットを半分切り捨てた形式です。同じ符号ビットと 8 ビットの指数部を保持しますが、23 ビットある仮数部のうち保持されるのは上位 7 ビットだけです。そのため、QBit カラムから最初の 16 ビットプレーンを読み出すことで、実質的に BFloat16 のメモリレイアウトを再現できます。したがって、この場合には参照ベクターを BFloat16 に安全に変換できます(実際にそうしています)。
Float64 の複雑さ
一方、Float64 は話が異なります。Float64 は 11 ビットの指数部と 52 ビットの仮数部を使用しており、単にビット数が 2 倍になった Float32 というわけではありません。その構造や指数バイアスはまったく異なります。Float64 を Float32 のような、より小さいフォーマットにダウンキャストするには、各値を最も近い表現可能な Float32 に丸める、正規の IEEE-754 変換が必要になります。この丸め処理は計算コストが高くなります。
DBpedia を用いた例
DBpedia データセットを用いた実世界の例で、QBit の動作を確認してみましょう。このデータセットには、Float32 形式の埋め込みベクトルとして表現された Wikipedia 記事が 100 万件含まれています。
セットアップ
まずテーブルを作成します
CREATE TABLE dbpedia
(
id String,
title String,
text String,
vector Array(Float32) CODEC(NONE)
) ENGINE = MergeTree ORDER BY (id);
コマンドラインからデータを挿入します:
for i in $(seq 0 25); do
echo "Processing file ${i}..."
clickhouse client -q "INSERT INTO dbpedia SELECT _id, title, text, \"text-embedding-3-large-1536-embedding\" FROM url('https://huggingface.co/api/datasets/Qdrant/dbpedia-entities-openai3-text-embedding-3-large-1536-1M/parquet/default/train/${i}.parquet') SETTINGS max_http_get_redirects=5,enable_url_encoding=0;"
echo "File ${i} complete."
done
ヒント
データの挿入には少し時間がかかるかもしれません。
コーヒーブレイクの時間です!
別の方法としては、25個の Parquet ファイルそれぞれを読み込むために、以下のように個々の SQL 文を実行することもできます。
INSERT INTO dbpedia SELECT _id, title, text, "text-embedding-3-large-1536-embedding" FROM url('https://huggingface.co/api/datasets/Qdrant/dbpedia-entities-openai3-text-embedding-3-large-1536-1M/parquet/default/train/0.parquet') SETTINGS max_http_get_redirects=5,enable_url_encoding=0;
INSERT INTO dbpedia SELECT _id, title, text, "text-embedding-3-large-1536-embedding" FROM url('https://huggingface.co/api/datasets/Qdrant/dbpedia-entities-openai3-text-embedding-3-large-1536-1M/parquet/default/train/1.parquet') SETTINGS max_http_get_redirects=5,enable_url_encoding=0;
...
INSERT INTO dbpedia SELECT _id, title, text, "text-embedding-3-large-1536-embedding" FROM url('https://huggingface.co/api/datasets/Qdrant/dbpedia-entities-openai3-text-embedding-3-large-1536-1M/parquet/default/train/25.parquet') SETTINGS max_http_get_redirects=5,enable_url_encoding=0;
dbpedia テーブルに 100 万行が存在することを確認します:
SELECT count(*)
FROM dbpedia
┌─count()─┐
│ 1000000 │
└─────────┘
次に QBit カラムを追加します。
SET allow_experimental_qbit_type = 1;
-- Assuming you have a table with Float32 embeddings
ALTER TABLE dbpedia ADD COLUMN qbit QBit(Float32, 1536);
ALTER TABLE dbpedia UPDATE qbit = vector WHERE 1;
検索クエリ
Moon、Apollo 11、Space Shuttle、Astronaut、Rocket といった宇宙関連の検索語すべてに対して、最も関連性の高い概念を探してみます。
SELECT
title,
text,
COUNT(DISTINCT concept) AS num_concepts_matched,
MIN(distance) AS min_distance,
AVG(distance) AS avg_distance
FROM (
(
SELECT title, text, 'Moon' AS concept,
L2DistanceTransposed(qbit, (SELECT vector FROM dbpedia WHERE title = 'Moon'), 5) AS distance
FROM dbpedia
WHERE title != 'Moon'
ORDER BY distance ASC
LIMIT 1000
)
UNION ALL
(
SELECT title, text, 'Apollo 11' AS concept,
L2DistanceTransposed(qbit, (SELECT vector FROM dbpedia WHERE title = 'Apollo 11'), 5) AS distance
FROM dbpedia
WHERE title != 'Apollo 11'
ORDER BY distance ASC
LIMIT 1000
)
UNION ALL
(
SELECT title, text, 'Space Shuttle' AS concept,
L2DistanceTransposed(qbit, (SELECT vector FROM dbpedia WHERE title = 'Space Shuttle'), 5) AS distance
FROM dbpedia
WHERE title != 'Space Shuttle'
ORDER BY distance ASC
LIMIT 1000
)
UNION ALL
(
SELECT title, text, 'Astronaut' AS concept,
L2DistanceTransposed(qbit, (SELECT vector FROM dbpedia WHERE title = 'Astronaut'), 5) AS distance
FROM dbpedia
WHERE title != 'Astronaut'
ORDER BY distance ASC
LIMIT 1000
)
UNION ALL
(
SELECT title, text, 'Rocket' AS concept,
L2DistanceTransposed(qbit, (SELECT vector FROM dbpedia WHERE title = 'Rocket'), 5) AS distance
FROM dbpedia
WHERE title != 'Rocket'
ORDER BY distance ASC
LIMIT 1000
)
)
WHERE title NOT IN ('Moon', 'Apollo 11', 'Space Shuttle', 'Astronaut', 'Rocket')
GROUP BY title, text
HAVING num_concepts_matched >= 3
ORDER BY num_concepts_matched DESC, min_distance ASC
LIMIT 10;
このクエリは、5 つの各コンセプトごとに、意味的に類似した上位 1000 件のエントリを検索します。
そのうち少なくとも 3 つの結果に現れるエントリを返し、マッチしたコンセプトの数と、それらのいずれかとの最小距離(元のコンセプトは除外)に基づいて順位付けします。
わずか 5 ビット(符号 1 ビット + 指数 4 ビット、仮数部は 0)だけを使用します:
Row 1:
──────
title: Aintree railway station
text: For a guide to the various Aintree stations that have existed and their relationship to each other see Aintree Stations.Aintree railway station is a railway station in Aintree, Merseyside, England. It is on the Ormskirk branch of the Merseyrail network's Northern Line. Until 1968 it was known as Aintree Sefton Arms after a nearby public house. The station's design reflects the fact it is the closest station to Aintree Racecourse, where the annual Grand National horse race takes place.
num_concepts_matched: 5
min_distance: 0.9971279086553189
avg_distance: 0.9972260772085877
Row 2:
──────
title: AP German Language
text: Advanced Placement German Language (also known as AP German Language or AP German) is a course and examination provided by the College Board through the Advanced Placement Program. This course is designed to give high school students the opportunity to receive credit in a college-level German language course.Originally the College Board had offered two AP German exams, one with AP German Language and another with AP German Literature.
num_concepts_matched: 5
min_distance: 0.9971279086553189
avg_distance: 0.9972260772085877
Row 3:
──────
title: Adelospondyli
text: Adelospondyli is an order of elongate, presumably aquatic, Carboniferous amphibians. The skull is solidly roofed, and elongate, with the orbits located very far forward. The limbs are well developed. Most adelospondyls belong to the family Adelogyrinidae, although the adelospondyl Acherontiscus has been placed in its own family, Acherontiscidae. The group is restricted to the Mississippian (Serpukhovian Age) of Scotland.
num_concepts_matched: 5
min_distance: 0.9971279086553189
avg_distance: 0.9972260772085877
Row 4:
──────
title: Adrien-Henri de Jussieu
text: Adrien-Henri de Jussieu (23 December 1797 – 29 June 1853) was a French botanist.Born in Paris as the son of botanist Antoine Laurent de Jussieu, he received the degree of Doctor of Medicine in 1824 with a treatise of the plant family Euphorbiaceae. When his father retired in 1826, he succeeded him at the Jardin des Plantes; in 1845 he became professor of organography of plants.
num_concepts_matched: 5
min_distance: 0.9971279086553189
avg_distance: 0.9972260772085877
Row 5:
──────
title: Alan Taylor (footballer, born 1953)
text: Alan Taylor (born 14 November 1953) is an English former professional footballer best known for his goalscoring exploits with West Ham United in their FA Cup success of 1975, culminating in two goals in that season's final.
num_concepts_matched: 5
min_distance: 0.9971279086553189
avg_distance: 0.9972260772085877
Row 6:
──────
title: Abstract algebraic logic
text: In mathematical logic, abstract algebraic logic is the study of the algebraization of deductive systemsarising as an abstraction of the well-known Lindenbaum-Tarski algebra, and how the resulting algebras are related to logical systems.
num_concepts_matched: 5
min_distance: 0.9971279086553189
avg_distance: 0.9972260772085877
Row 7:
──────
title: Ahsan Saleem Hyat
text: General Ahsan Saleem Hayat (Urdu: احسن سلیم حیات; born 10 January 1948), is a retired four-star general who served as the vice chief of army staff of the Pakistan Army from 2004 until his retirement in 2007. Prior to that, he served as the operational field commander of the V Corps in Sindh Province and was a full-tenured professor of war studies at the National Defence University. He was succeeded by General Ashfaq Parvez Kayani on 8 October 2007.
num_concepts_matched: 5
min_distance: 0.9971279086553189
avg_distance: 0.9972260772085877
Row 8:
──────
title: Al Wafa al Igatha al Islamia
text: There is another organization named Al Wafa (Israel), a charity, in Israel, devoted to womenThere is another organization Jamaiat Al-Wafa LiRayat Al-Musenin which is proscribed by the Israeli government.Al Wafa is an Islamic charity listed in Executive Order 13224 as an entity that supports terrorism.United States intelligence officials state that it was founded in Afghanistan by Adil Zamil Abdull Mohssin Al Zamil,Abdul Aziz al-Matrafi and Samar Khand.According to Saad Madai Saad al-Azmi's Combatant Status Review Tribunal Al Wafa is located in the Wazir Akhbar Khan area ofAfghanistan.
num_concepts_matched: 5
min_distance: 0.9971279086553189
avg_distance: 0.9972260772085877
Row 9:
───────
title: Alex Baumann
text: Alexander Baumann, OC OOnt (born April 21, 1964) is a Canadian former competitive swimmer who won two gold medals and set two world records at the 1984 Summer Olympics in Los Angeles.Born in Prague (former Czechoslovakia), Baumann was raised in Canada after his family moved there in 1969 following the Prague Spring.
num_concepts_matched: 5
min_distance: 0.9971279086553189
avg_distance: 0.9972260772085877
Row 10:
───────
title: Alberni-Clayoquot Regional District
text: The Alberni-Clayoquot Regional District (2006 population 30,664) of British Columbia is located on west central Vancouver Island. Adjacent regional districts it shares borders with are the Strathcona and Comox Valley Regional Districts to the north, and the Nanaimo and Cowichan Valley Regional Districts to the east. The regional district offices are located in Port Alberni.
num_concepts_matched: 5
min_distance: 0.9971279086553189
avg_distance: 0.9972260772085877
10 rows in set. Elapsed: 0.542 sec. Processed 5.01 million rows, 1.86 GB (9.24 million rows/s., 3.43 GB/s.)
Peak memory usage: 327.04 MiB.
パフォーマンス: セット内の 10 行。経過時間: 0.271 秒。処理件数: 846 万行 / 4.54 GB(毎秒 3,119 万行、16.75 GB/秒)。ピークメモリ使用量: 739.82 MiB。
ブルートフォース検索との性能比較
SELECT
title,
text,
COUNT(DISTINCT concept) AS num_concepts_matched,
MIN(distance) AS min_distance,
AVG(distance) AS avg_distance
FROM (
(
SELECT title, text, 'Moon' AS concept,
L2DistanceTransposed(qbit, (SELECT vector FROM dbpedia WHERE title = 'Moon'), 5) AS distance
FROM dbpedia
WHERE title != 'Moon'
ORDER BY distance ASC
LIMIT 1000
)
UNION ALL
(
SELECT title, text, 'Apollo 11' AS concept,
L2DistanceTransposed(qbit, (SELECT vector FROM dbpedia WHERE title = 'Apollo 11'), 5) AS distance
FROM dbpedia
WHERE title != 'Apollo 11'
ORDER BY distance ASC
LIMIT 1000
)
UNION ALL
(
SELECT title, text, 'Space Shuttle' AS concept,
L2DistanceTransposed(qbit, (SELECT vector FROM dbpedia WHERE title = 'Space Shuttle'), 5) AS distance
FROM dbpedia
WHERE title != 'Space Shuttle'
ORDER BY distance ASC
LIMIT 1000
)
UNION ALL
(
SELECT title, text, 'Astronaut' AS concept,
L2DistanceTransposed(qbit, (SELECT vector FROM dbpedia WHERE title = 'Astronaut'), 5) AS distance
FROM dbpedia
WHERE title != 'Astronaut'
ORDER BY distance ASC
LIMIT 1000
)
UNION ALL
(
SELECT title, text, 'Rocket' AS concept,
L2DistanceTransposed(qbit, (SELECT vector FROM dbpedia WHERE title = 'Rocket'), 5) AS distance
FROM dbpedia
WHERE title != 'Rocket'
ORDER BY distance ASC
LIMIT 1000
)
)
WHERE title NOT IN ('Moon', 'Apollo 11', 'Space Shuttle', 'Astronaut', 'Rocket')
GROUP BY title, text
HAVING num_concepts_matched >= 3
ORDER BY num_concepts_matched DESC, min_distance ASC
LIMIT 10;
Row 1:
──────
title: Apollo program
text: The Apollo program, also known as Project Apollo, was the third United States human spaceflight program carried out by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), which accomplished landing the first humans on the Moon from 1969 to 1972. First conceived during Dwight D. Eisenhower's administration as a three-man spacecraft to follow the one-man Project Mercury which put the first Americans in space, Apollo was later dedicated to President John F.
num_concepts_matched: 4
min_distance: 0.82420665
avg_distance: 1.0207901149988174
Row 2:
──────
title: Apollo 8
text: Apollo 8, the second human spaceflight mission in the United States Apollo space program, was launched on December 21, 1968, and became the first manned spacecraft to leave Earth orbit, reach the Earth's Moon, orbit it and return safely to Earth.
num_concepts_matched: 4
min_distance: 0.8285278
avg_distance: 1.0357224345207214
Row 3:
──────
title: Lunar Orbiter 1
text: The Lunar Orbiter 1 robotic (unmanned) spacecraft, part of the Lunar Orbiter Program, was the first American spacecraft to orbit the Moon. It was designed primarily to photograph smooth areas of the lunar surface for selection and verification of safe landing sites for the Surveyor and Apollo missions. It was also equipped to collect selenodetic, radiation intensity, and micrometeoroid impact data.The spacecraft was placed in an Earth parking orbit on August 10, 1966 at 19:31 (UTC).
num_concepts_matched: 4
min_distance: 0.94581836
avg_distance: 1.0584313124418259
Row 4:
──────
title: Apollo (spacecraft)
text: The Apollo spacecraft was composed of three parts designed to accomplish the American Apollo program's goal of landing astronauts on the Moon by the end of the 1960s and returning them safely to Earth. The expendable (single-use) spacecraft consisted of a combined Command/Service Module (CSM) and a Lunar Module (LM).
num_concepts_matched: 4
min_distance: 0.9643517
avg_distance: 1.0367188602685928
Row 5:
──────
title: Surveyor 1
text: Surveyor 1 was the first lunar soft-lander in the unmanned Surveyor program of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA, United States). This lunar soft-lander gathered data about the lunar surface that would be needed for the manned Apollo Moon landings that began in 1969.
num_concepts_matched: 4
min_distance: 0.9738264
avg_distance: 1.0988530814647675
Row 6:
──────
title: Spaceflight
text: Spaceflight (also written space flight) is ballistic flight into or through outer space. Spaceflight can occur with spacecraft with or without humans on board. Examples of human spaceflight include the Russian Soyuz program, the U.S. Space shuttle program, as well as the ongoing International Space Station. Examples of unmanned spaceflight include space probes that leave Earth orbit, as well as satellites in orbit around Earth, such as communications satellites.
num_concepts_matched: 4
min_distance: 0.9831049
avg_distance: 1.060678943991661
Row 7:
──────
title: Skylab
text: Skylab was a space station launched and operated by NASA and was the United States' first space station. Skylab orbited the Earth from 1973 to 1979, and included a workshop, a solar observatory, and other systems. It was launched unmanned by a modified Saturn V rocket, with a weight of 169,950 pounds (77 t). Three manned missions to the station, conducted between 1973 and 1974 using the Apollo Command/Service Module (CSM) atop the smaller Saturn IB, each delivered a three-astronaut crew.
num_concepts_matched: 4
min_distance: 0.99155205
avg_distance: 1.0769911855459213
Row 8:
──────
title: Orbital spaceflight
text: An orbital spaceflight (or orbital flight) is a spaceflight in which a spacecraft is placed on a trajectory where it could remain in space for at least one orbit. To do this around the Earth, it must be on a free trajectory which has an altitude at perigee (altitude at closest approach) above 100 kilometers (62 mi) (this is, by at least one convention, the boundary of space). To remain in orbit at this altitude requires an orbital speed of ~7.8 km/s.
num_concepts_matched: 4
min_distance: 1.0075209
avg_distance: 1.085978478193283
Row 9:
───────
title: Dragon (spacecraft)
text: Dragon is a partially reusable spacecraft developed by SpaceX, an American private space transportation company based in Hawthorne, California. Dragon is launched into space by the SpaceX Falcon 9 two-stage-to-orbit launch vehicle, and SpaceX is developing a crewed version called the Dragon V2.During its maiden flight in December 2010, Dragon became the first commercially built and operated spacecraft to be recovered successfully from orbit.
num_concepts_matched: 4
min_distance: 1.0222818
avg_distance: 1.0942841172218323
Row 10:
───────
title: Space capsule
text: A space capsule is an often manned spacecraft which has a simple shape for the main section, without any wings or other features to create lift during atmospheric reentry.Capsules have been used in most of the manned space programs to date, including the world's first manned spacecraft Vostok and Mercury, as well as in later Soviet Voskhod, Soyuz, Zond/L1, L3, TKS, US Gemini, Apollo Command Module, Chinese Shenzhou and US, Russian and Indian manned spacecraft currently being developed.
num_concepts_matched: 4
min_distance: 1.0262821
avg_distance: 1.0882147550582886
パフォーマンス: 10行のセット。経過時間: 1.157秒。処理済み: 1000万行、32.76 GB (864万行/秒、28.32 GB/秒)。ピークメモリ使用量: 6.05 GiB。
重要なインサイト
結果はどうだったでしょうか? 単に良いどころではありません。驚くほど良好でした。浮動小数点数から仮数部全体と指数部の半分を取り除いても、依然として意味のある情報が保持されるとは、直感的には思えません。
QBit の核心となるインサイトは、「重要でないビットを無視してもベクトル検索は機能する」という点です。
メモリ使用量は、優れたセマンティック検索品質を維持したまま、6.05 GB から 740 MB へと削減されました!
QBit は、浮動小数点数をビットプレーンとして保存するカラム型です。
ベクトル検索の際に読み出すビット数を選択できるため、データを変更することなく、再現率とパフォーマンスを調整できます。
各ベクトル検索手法には、それぞれ再現率、精度、パフォーマンスのトレードオフを決める固有のパラメータがあります。
通常は、これらをあらかじめ選択しておく必要があります。
もし選択を誤ると、多くの時間とリソースが無駄になり、後から方針を変えるのが困難になります。
QBit を使えば、こうした事前の意思決定は不要です。
クエリ実行時に直接、精度と速度のトレードオフを調整できるため、進めながら最適なバランスを探ることができます。
Raufs Dunamalijevs による ブログ記事(2025 年 10 月 28 日公開)を基にした内容です